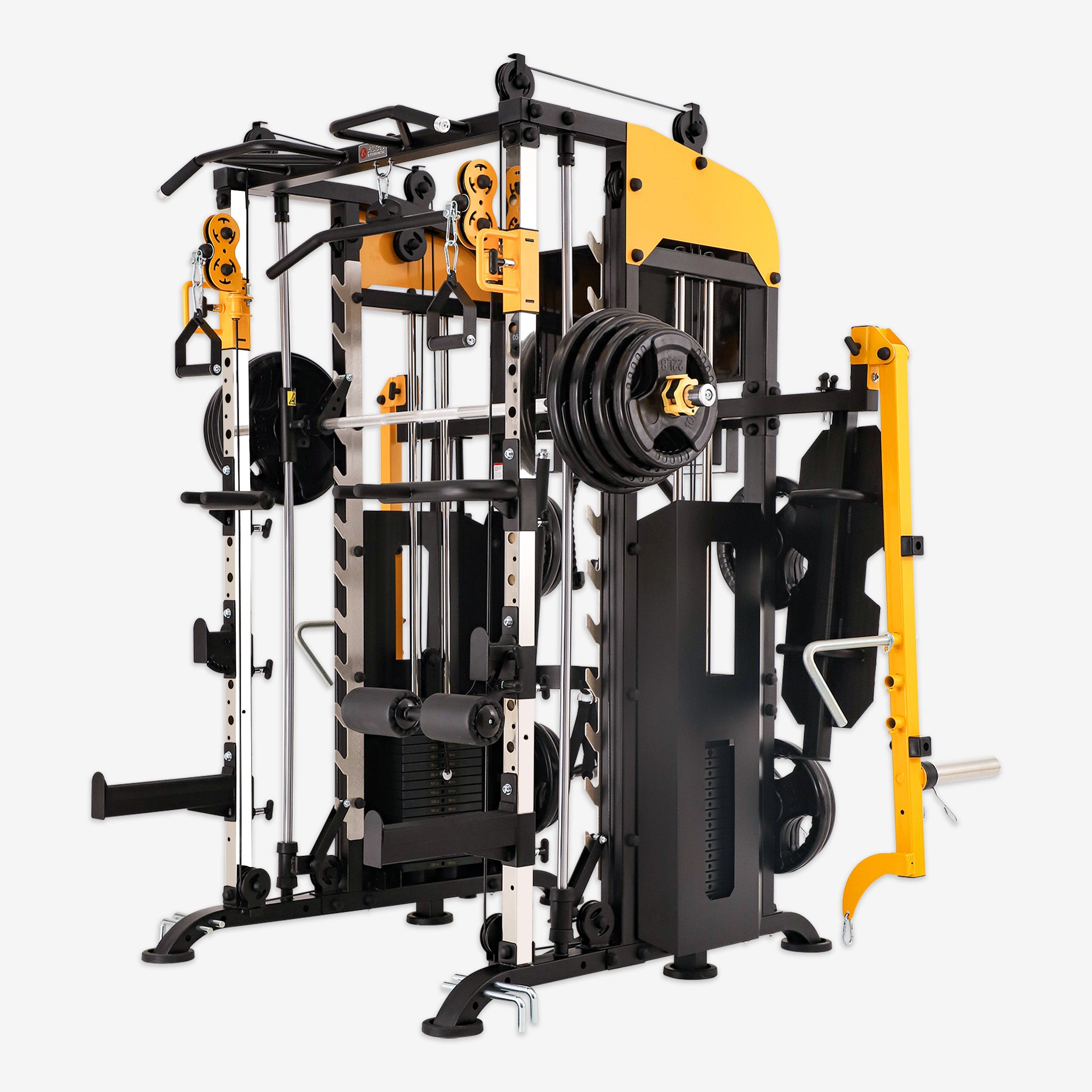
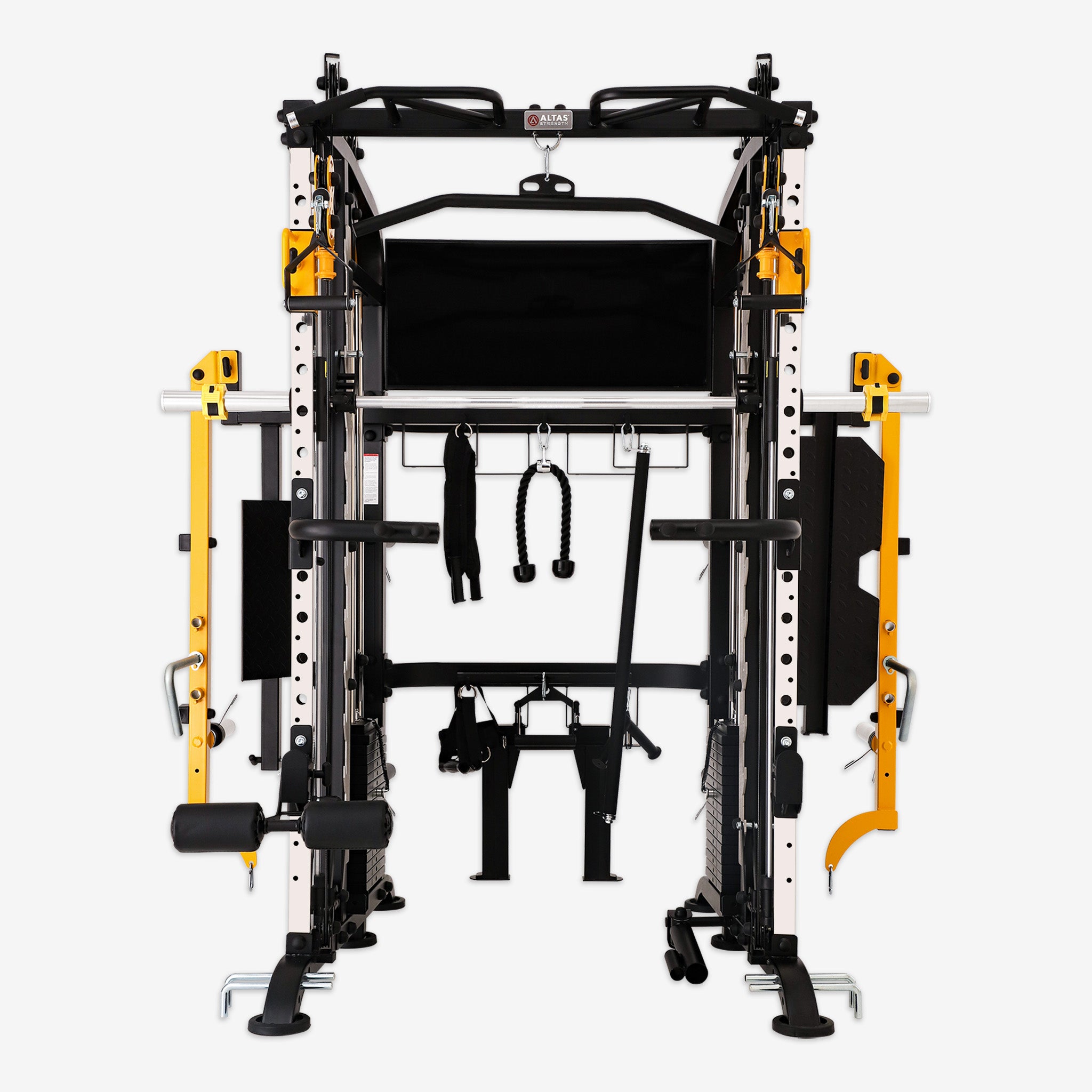
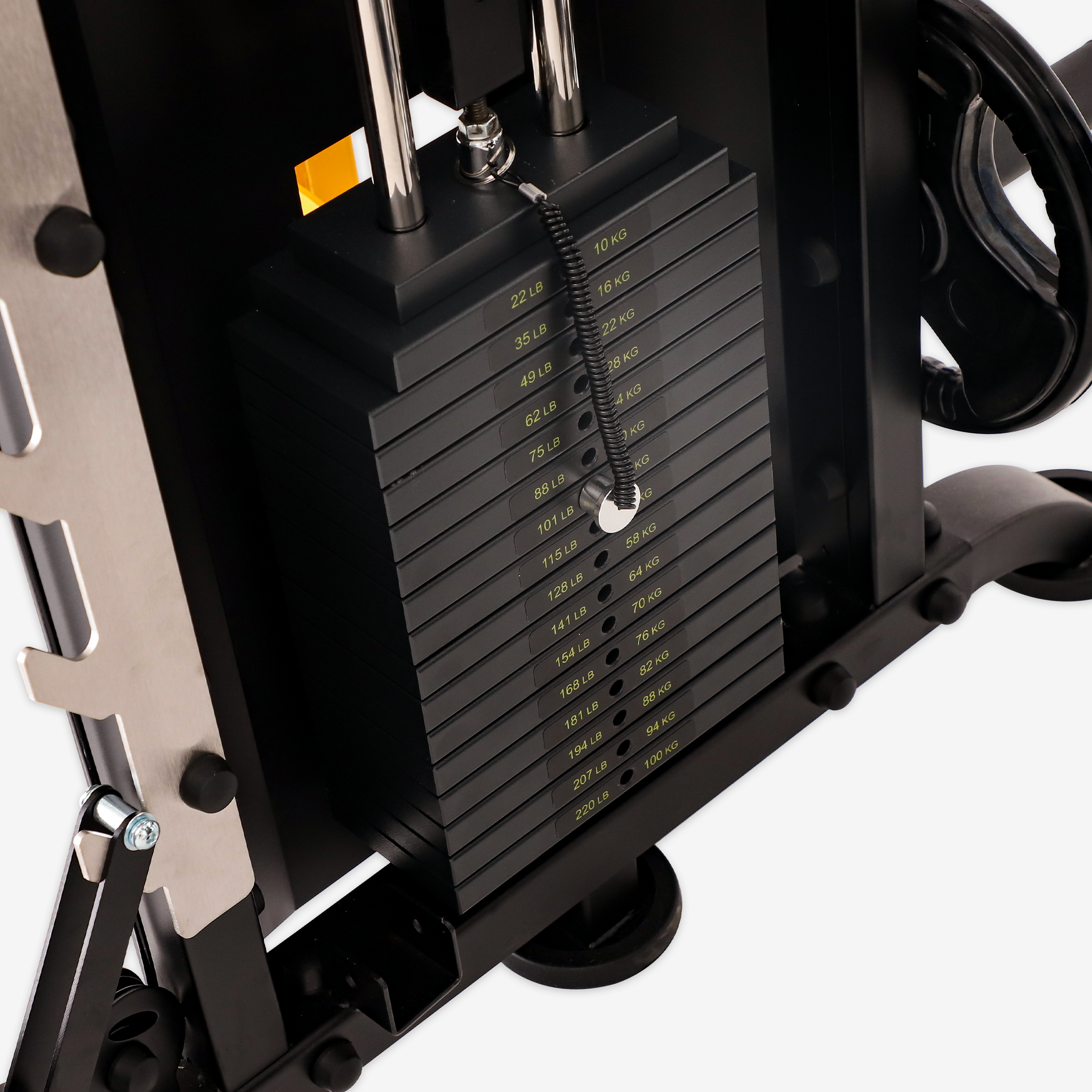
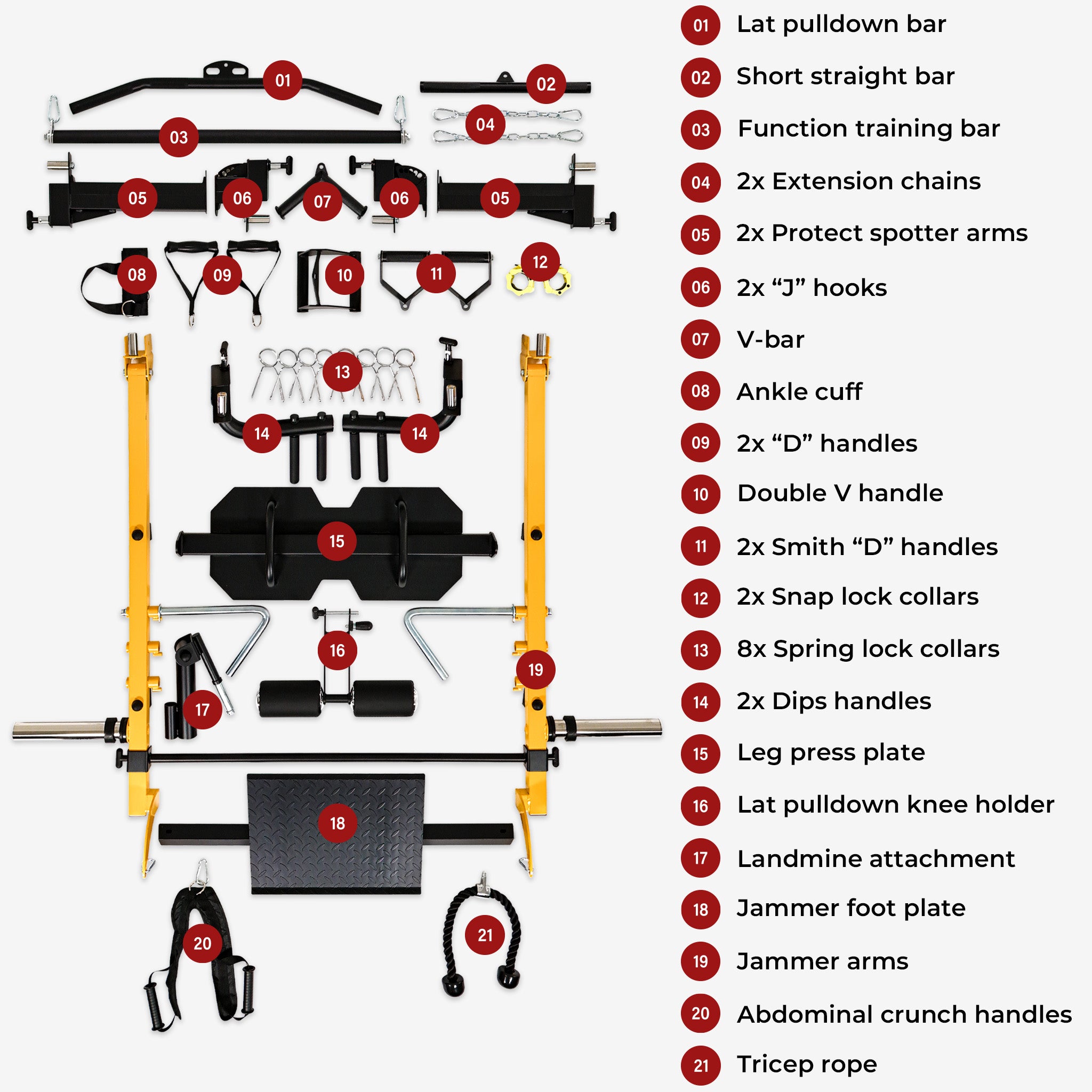
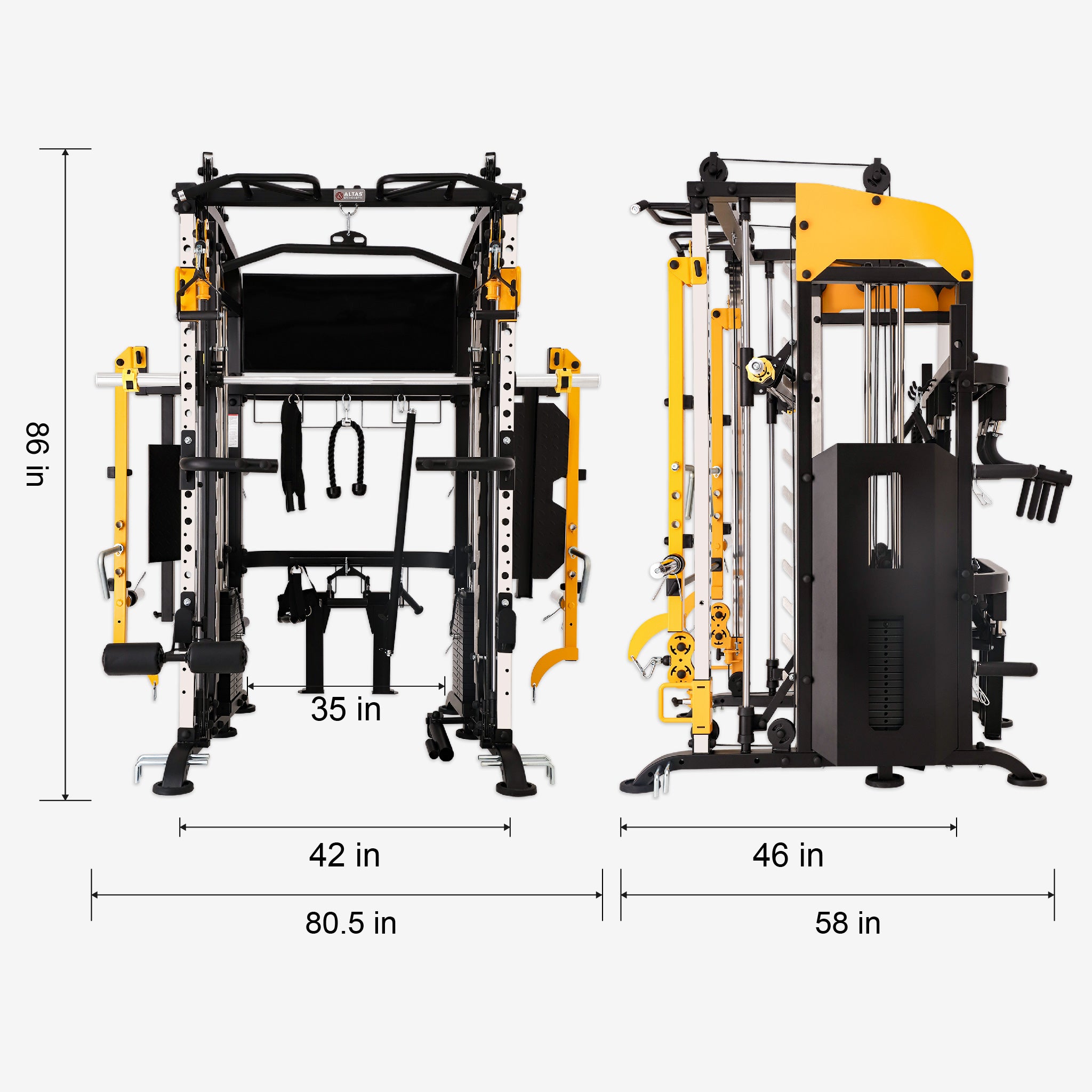
The back is the “support pillar” of the human body. A strong back not only promotes good posture but also enhances athletic performance and daily comfort. Back training machines, with controllable resistance, guided tracks, and built-in safety features, are now staples in both gyms and home fitness setups. Here’s how they help you achieve a stronger, healthier back.
Core Advantages
1. Efficient Enhancement of Back Strength and Muscle Thickness
Machines like seated rows, lat pulldowns, and back extensions deeply stimulate large back muscles such as the lats, traps, and rhomboids. Adjustable resistance allows progressive overload, enabling users to safely lift heavier weights and build both strength and muscle volume.
2. Posture Improvement and Prevention of Hunchback
Strengthening the back muscles flattens the shoulder blades and corrects poor postures like rounded shoulders or a hunched chest. Regular training can reduce lower back pain and help maintain the spine's natural curvature, giving a taller and more upright appearance.
3. Enhanced Core Stability and Overall Athletic Performance
Back machines not only target back muscles but also activate the glutes, hamstrings, and core, improving overall stability and balance. A strong back enhances performance in weightlifting, running, jumping, and other athletic activities.
4. Reduced Risk of Injury
The guided tracks and safety guards reduce postural errors and the risk of losing control, especially compared to free weights. Progressive loading ensures safer intensity increases, minimizing muscle strains and joint injuries.
5. Metabolic Boost and Fat Loss Assistance
Back muscles cover a large area, so building them can boost basal metabolic rate and daily calorie expenditure. Combining machine-based back workouts with cardio accelerates fat burning while sculpting a toned back.
6. Training Convenience and Diversity
Gyms offer a variety of back machines to target different muscles, preventing workout monotony. At home, adjustable cable machines or foldable back extension machines provide safe, controllable training even in limited spaces.
Common Back Training Machines and Suitable Users
- Seated Lat Pulldown: Targets lats and traps; ideal for beginners and those seeking back width, with adjustable resistance to reduce shoulder strain.
- Seated Row: Focuses on middle back and rhomboids; suitable for building back thickness with low-impact heavy-weight options.
- Back Extension: Strengthens lower back and glutes; recommended for posture improvement and those with lower back discomfort.
- T-Bar Row: Engages upper back and scapular muscles; ideal for advanced users to enhance upper-back stability.
- Multi-functional Cable Machine: Works the entire back and shoulders; great for home gyms with adjustable resistance and multi-angle training.
Usage Suggestions
- Warm-up: 5–10 minutes of full-body warm-up to reduce injury risk.
- Proper Form: Keep chest up, retract shoulder blades, and avoid momentum-based movements.
- Progressive Loading: Start with light resistance, 8–12 reps per set, gradually increasing weight.
- Training Frequency: 1–2 dedicated back sessions per week, combined with other muscle groups.
- Complement Free Weights: Incorporate free weight exercises to further improve synergistic muscle control.
Conclusion
Back training machines provide a safe, controllable, and highly effective solution to strengthen the back, improve posture, enhance core stability, and boost metabolism. Whether for home or gym use, proper application of these machines can help build a strong, upright, and resilient back, improving both athletic performance and quality of life. Make the back machine a key part of your fitness routine and unlock the benefits of a stronger, healthier posture.