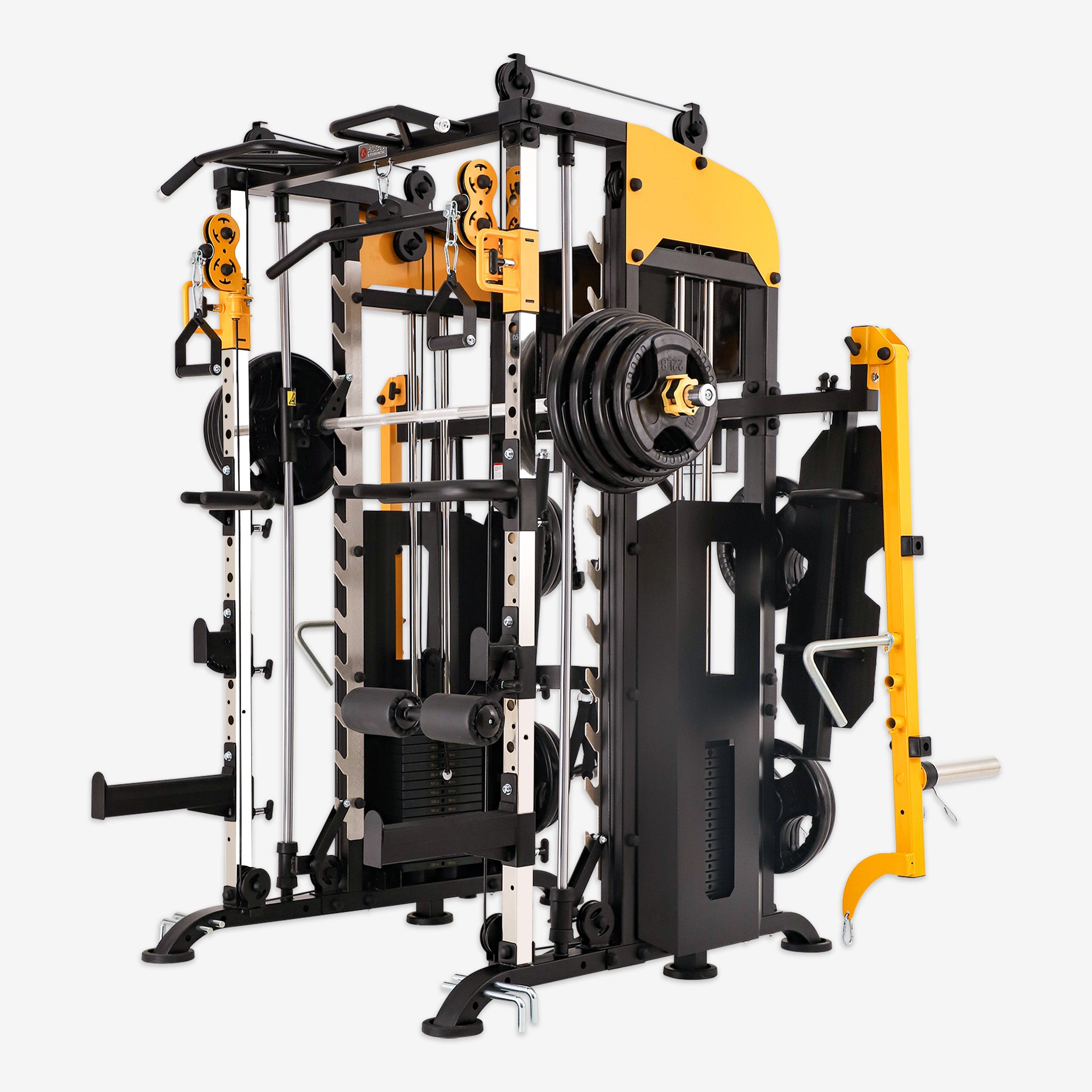
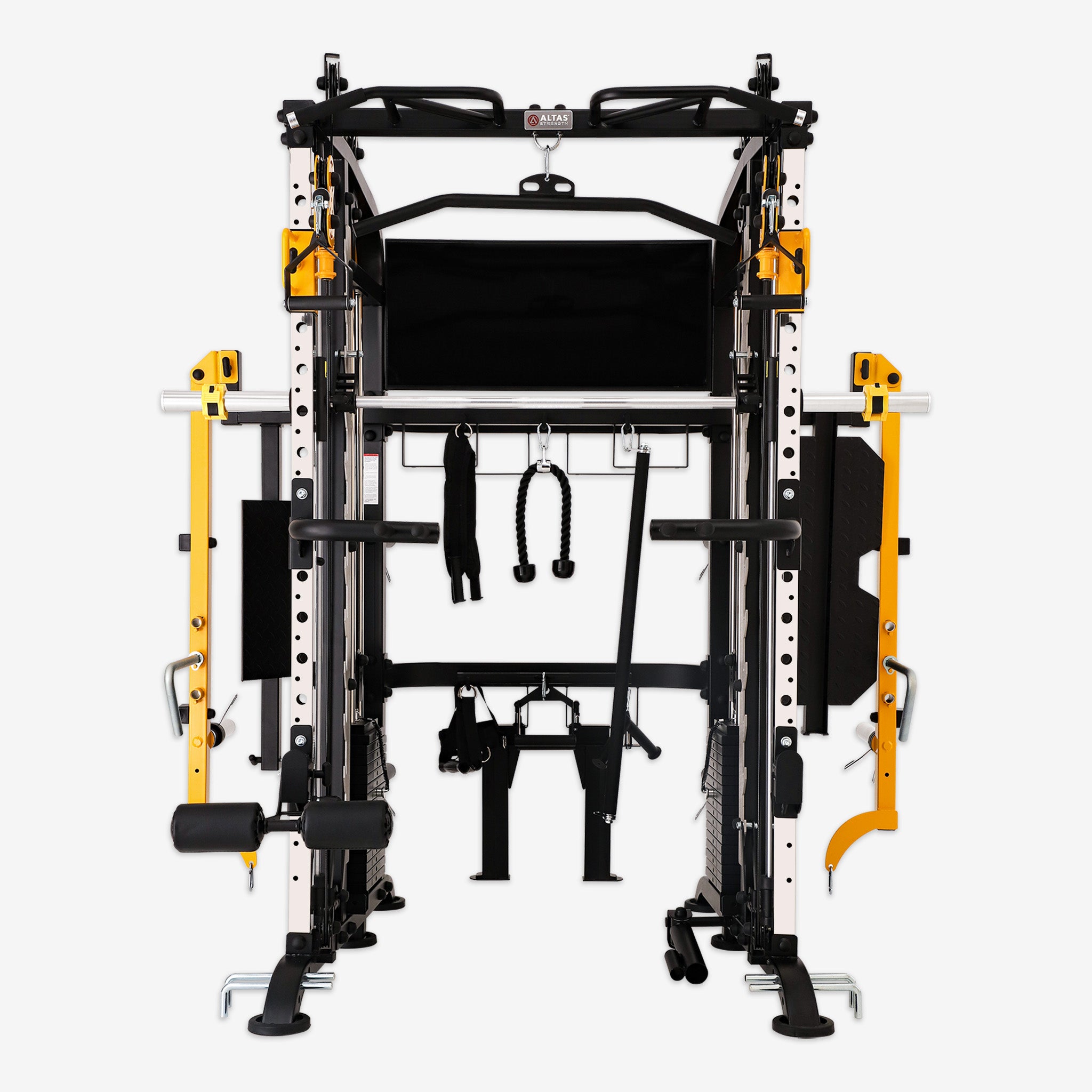
Bench Press: The Cornerstone of Strength Training
The bench press is a staple in strength training, recognized for building a powerful upper body. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced athlete, understanding its fundamentals, benefits, and safety precautions can elevate your fitness routine. In this guide, we’ll explore essential techniques, training advantages, safety considerations, and how to integrate the bench press into your workout regimen.
I. Fundamental Techniques of the Bench Press
Mastering the bench press requires precision and attention to form:
- Choose the Right Weight: Begin with manageable weights, gradually increasing as your strength improves.
- Adjust the Rack: Ensure the barbell is positioned over your chest, with your feet firmly planted and back stable.
- Grip Placement: Position hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, gripping the bar securely.
- Control Your Breathing: Inhale deeply before starting, holding your breath to stabilize your core.
- Lower the Barbell: Bring the bar to your chest in a controlled descent, elbows at a 90-degree angle.
- Push the Bar Up: Extend your arms fully to return to the starting position, exhaling at the top.
II. Training Benefits of the Bench Press
The bench press is more than just a chest workout:
- Strengthens Chest Muscles: Builds the pectoral muscles for a defined upper body.
- Enhances Shoulder Stability: Supports the rotator cuff, improving stability.
- Develops Arm Muscles: Particularly effective for triceps strength.
- Boosts Coordination: Engages core, back, and legs, promoting full-body synergy.
- Improves Muscular Endurance: Regular practice enhances stamina and performance.
III. Safety Considerations for the Bench Press
To minimize injury risk:
- Warm-Up Thoroughly: Prepare shoulder and chest muscles to prevent strain.
- Use Appropriate Weights: Avoid overloading; prioritize form over heavy lifting.
- Maintain Proper Elbow Position: Keep elbows aligned to reduce shoulder strain.
- Ensure Core Stability: Engage your core for spinal support.
- Use Safety Measures: Have a spotter or use a rack for added security.
IV. Integrating the Bench Press Into Your Routine
Strategize your training for maximum impact:
- Frequency: 1-2 sessions per week for beginners; 2-4 sets of 6-12 reps.
- Combine Exercises: Pair with flyes, shoulder presses, or tricep pushdowns.
- Variations: Incorporate incline, decline, and close-grip bench presses.
- Progress Gradually: Add weight over time while maintaining proper technique.
- Rest Adequately: Allow 24-48 hours for muscle recovery.
V. Advanced Bench Press Techniques
Elevate your routine with these methods:
- Pause Reps: Hold the barbell at the chest for increased muscle tension.
- Negative Training: Focus on slow descents with heavier weights.
- Tempo Variations: Alter lifting speeds for endurance and strength gains.
- Resistance Bands: Add bands for progressive resistance.
- Isometric Holds: Pause at different points to boost stability and endurance.
Conclusion
The bench press is indispensable for building strength, muscle definition, and coordination. By mastering the fundamentals, adhering to safety practices, and experimenting with advanced techniques, you can unlock the full potential of this classic exercise. Whether at home or in the gym, let the bench press propel you toward your fitness goals.
Explore premium strength training equipment at ALTAS Strength.