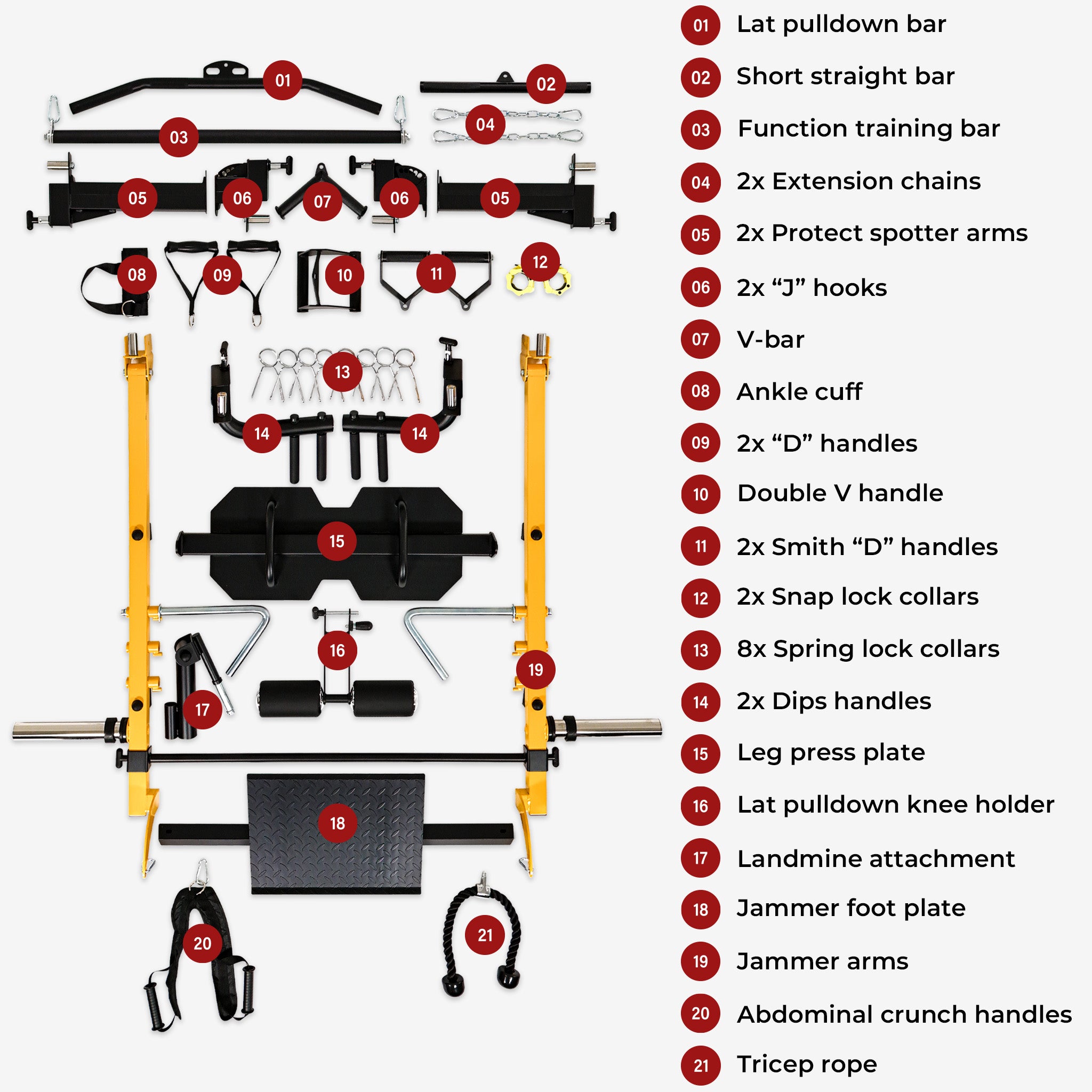
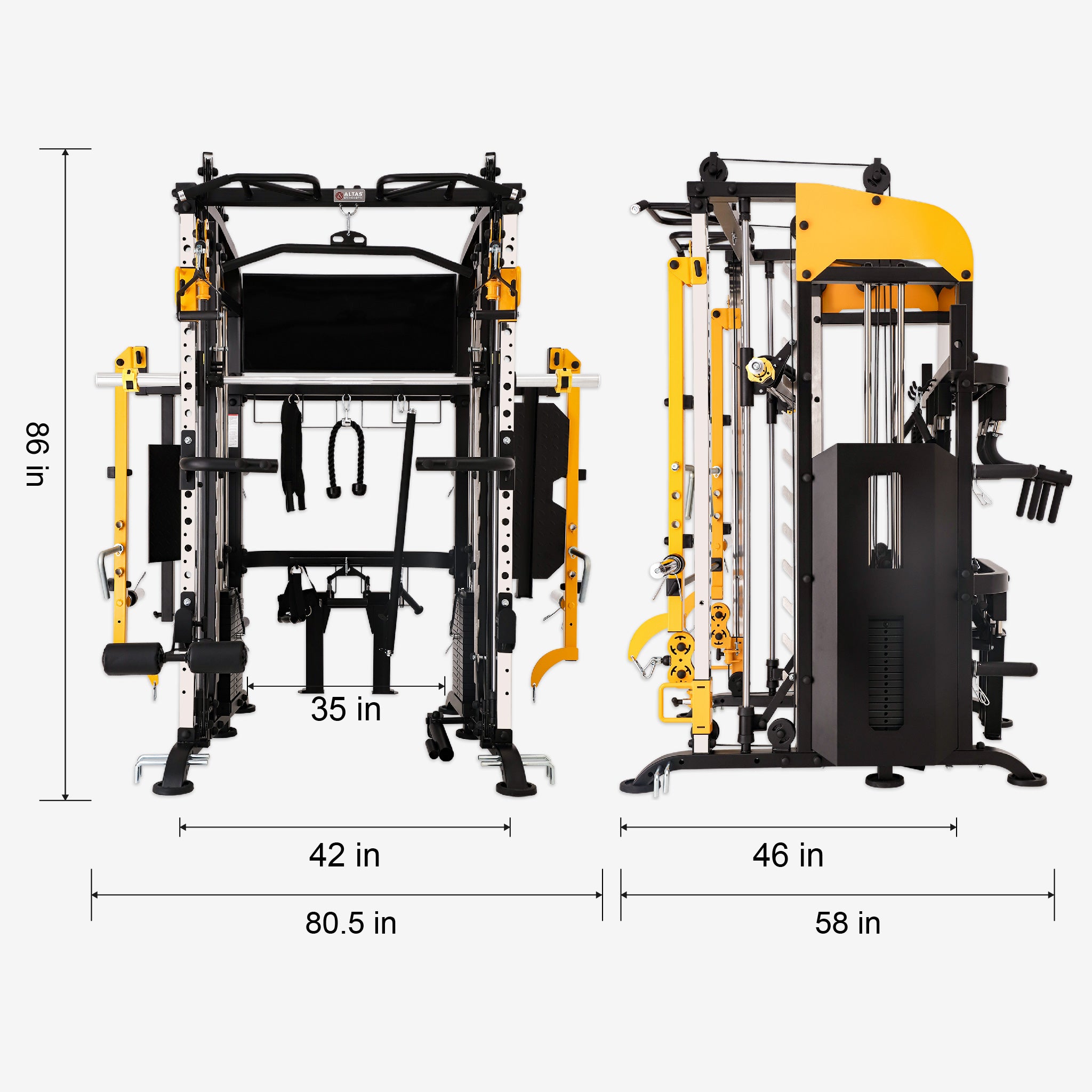
The oblique muscles are crucial for core stability, rotational power, and overall athletic performance. These muscles, including the internal and external obliques, work alongside the trapezius and scalene muscles to provide functional movement and prevent injuries. Understanding their anatomy, training methods, and recovery strategies can enhance performance and maintain long-term health.
Anatomy and Function of the Oblique Muscles
1. Internal and External Obliques: The Core’s Powerhouse
The external oblique muscles run diagonally from the ribs to the iliac crest, while the internal obliques run in the opposite direction. Together, they enable:
-
Trunk rotation and lateral flexion – Essential for twisting movements in sports like tennis, baseball, and boxing.
-
Core stability – Forming a natural corset with the transverse abdominis to protect the spine and maintain posture.
-
Breathing efficiency – Assisting the diaphragm during respiration.
2. Trapezius: The Upper Back Stabilizer
The trapezius, a large muscle spanning the upper back, plays a key role in stabilizing the shoulders and assisting in posture correction. Its three sections provide:
-
Upper fibers: Scapula elevation and head extension.
-
Middle fibers: Shoulder retraction and girdle stability.
-
Lower fibers: Scapula depression and shoulder joint coordination.
3. Scalenes: The Neck’s Hidden Guardians
Located in the neck, the scalene muscles support the cervical spine and assist in breathing. They function to:
-
Elevate the ribs during respiration.
-
Facilitate neck rotation and lateral flexion.
-
Stabilize the cervical spine and prevent nerve compression.
Best Exercises for Oblique and Core Strength
To develop a strong, stable core, focus on functional movements that engage the obliques, trapezius, and scalenes:
1. Oblique Strengthening Workouts
-
Russian Twists – Engages both internal and external obliques for rotational power.
-
Side Plank Holds – Improves core endurance and lateral stability.
-
Mountain Climbers – Activates the obliques dynamically for functional strength.
2. Trapezius Training for Core Stability
-
Incline Shrugs – Strengthens the upper trapezius and improves posture.
-
Wide-Grip Pull-Ups – Engages the middle trapezius for back stability.
-
Y-Raises – Activates the lower trapezius to support shoulder movement.
3. Scalene Muscle Conditioning
-
Neck Tilts and Rotations – Improves flexibility and prevents stiffness.
-
Fascial Rolling – Releases muscle tension and promotes blood circulation.
-
Postural Awareness Drills – Encourages a neutral head position to prevent forward-leaning posture.
Injury Prevention and Recovery Strategies
Overuse or improper training can lead to muscle imbalances and injuries. Implement these strategies to maintain muscle health:
-
Avoid Excessive Stretching During Rotational Movements – Prevents oblique muscle tears.
-
Incorporate Active Recovery Techniques – Foam rolling and stretching reduce stiffness.
-
Manage Posture Throughout the Day – Avoid prolonged forward head posture to reduce scalene strain.
-
Use Strengthening Exercises for Balance – Prevents muscle compensation that leads to misalignment.
Conclusion
The oblique muscles, along with the trapezius and scalenes, are essential for core stability, injury prevention, and optimal athletic performance. By incorporating targeted exercises, posture correction, and proper recovery strategies, you can enhance strength and movement efficiency. Explore high-quality strength equipment at Altas Strength to elevate your core training and unlock new performance potential.