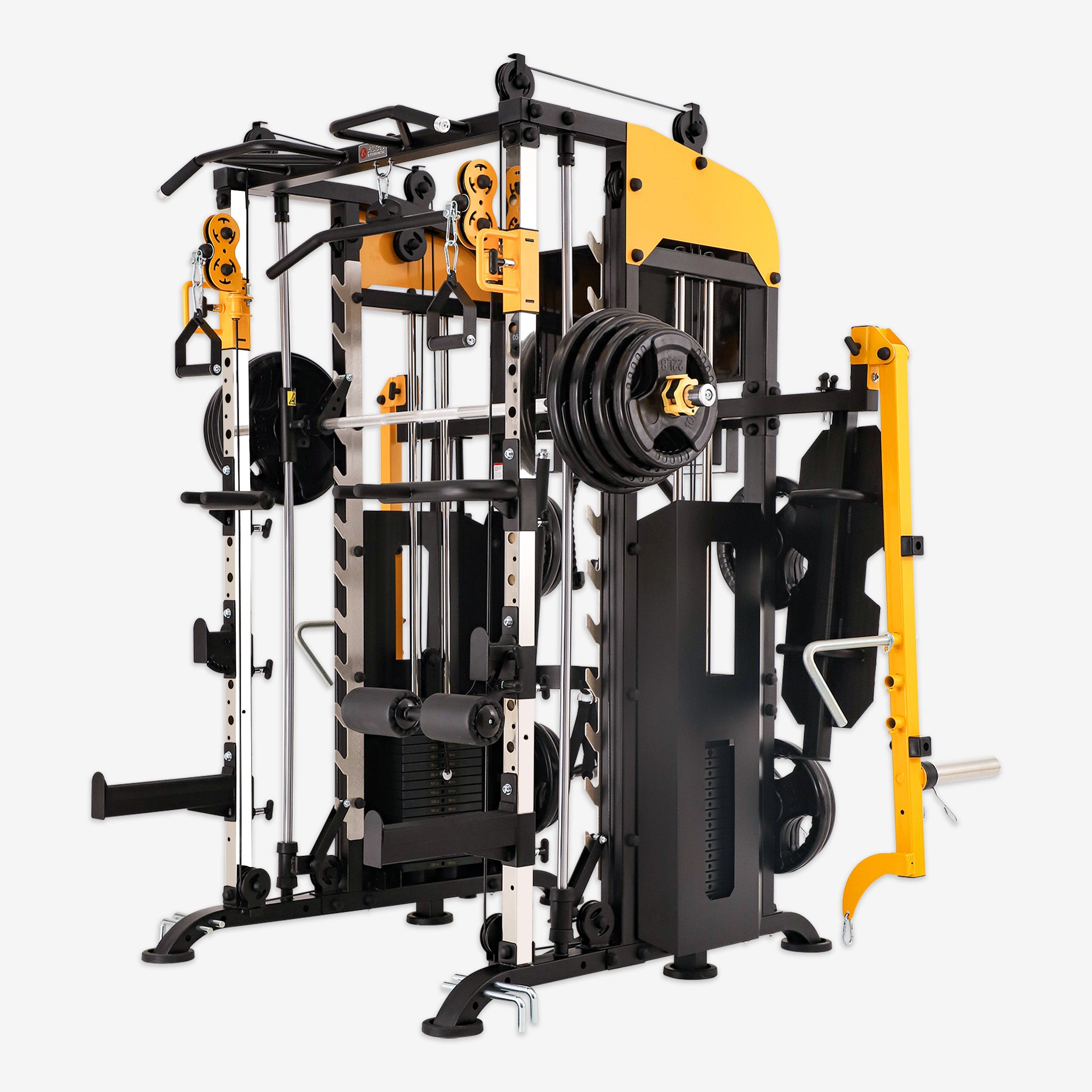
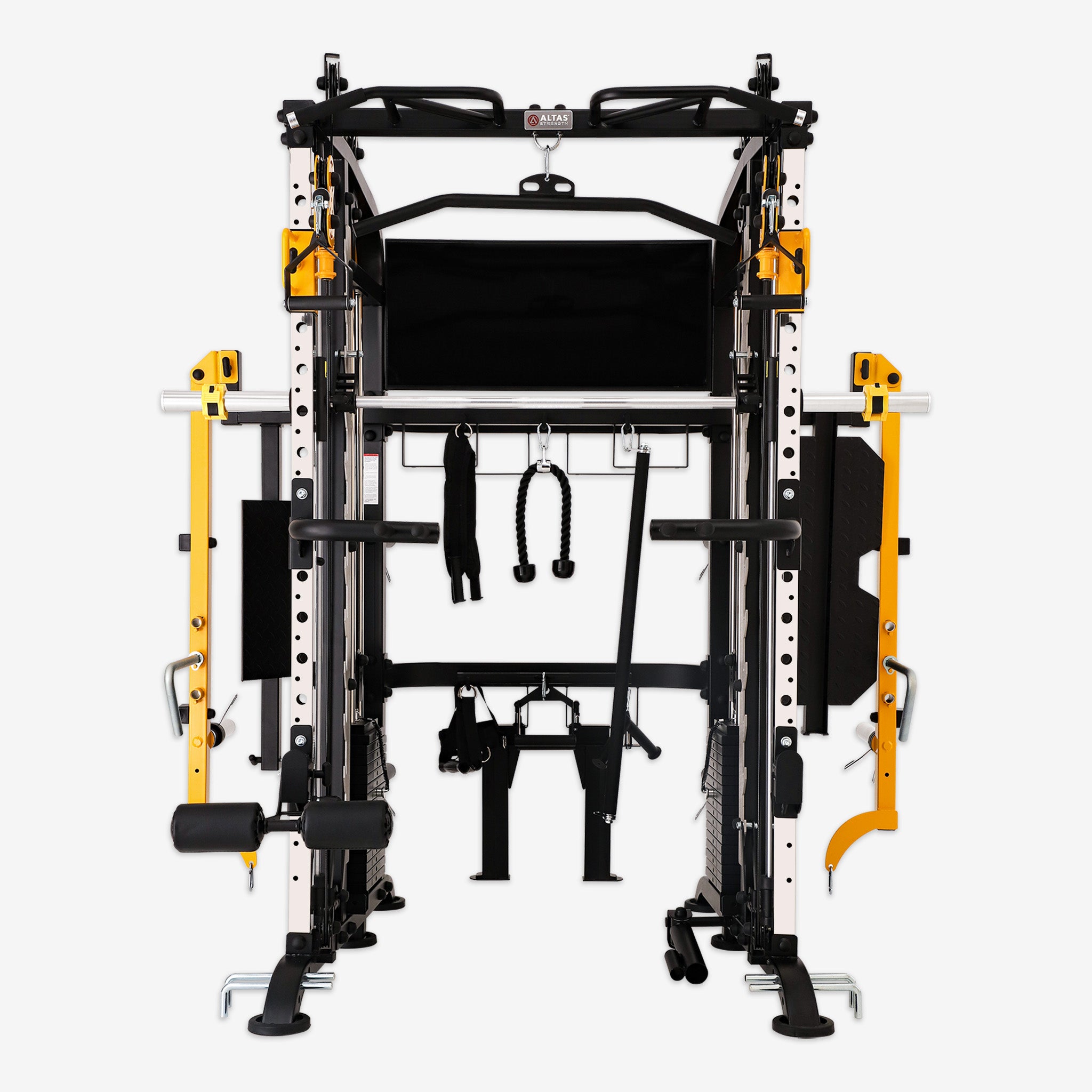
Deadlifts stand as a cornerstone exercise in strength training, renowned for their ability to engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously while fostering strength, stability, and overall athleticism. Let's delve into the myriad benefits of incorporating deadlifts into your workout routine and explore the key principles for mastering this fundamental movement.
1. Engagement of the Entire Musculature
Deadlifts are a compound movement that targets various muscle groups, including the posterior chain of the legs (hamstrings, glutes), the lumbar region, core musculature (rectus abdominis, obliques), as well as the muscles of the back, shoulders, and arms. This comprehensive engagement makes deadlifts an efficient full-body exercise, promoting balanced muscular development and functional strength.
2. Enhancement of Strength and Explosiveness
By lifting and lowering substantial weights, deadlifts effectively strengthen the leg and gluteal muscles, enhancing bodily explosiveness and power. Progressive overload, achieved through gradual increases in weight lifted, facilitates continuous strength gains, ultimately improving athletic performance and the ability to execute daily activities with ease.
3. Stability and Equilibrium of the Core Musculature
Maintaining stability within the core musculature is essential during deadlifts to uphold proper posture and balance. This not only reduces the risk of injury but also enhances stability and strength output in other physical activities, contributing to overall functional fitness and performance.
4. Amelioration of Spinal Health
Prudent execution of deadlifts strengthens the musculature of the back and spinal column, promoting spinal stability and health. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with sedentary lifestyles or those prone to spinal-related discomfort, as deadlifts help alleviate pain and improve overall spinal health.
5. Functional Training
Deadlifts mimic movements commonly encountered in daily life and sports, such as lifting heavy objects and performing bending actions. By incorporating deadlift training into your regimen, you can bolster the muscular strength and stability necessary for these functional movements, thereby enhancing both quality of life and athletic performance.
The Primary Procedural Sequence of Deadlifts
Mastering proper form is crucial for maximizing the benefits of deadlifts while minimizing the risk of injury. Follow these steps for safe and effective execution:
-
Initial Posture: Stand with feet parallel or slightly narrower, grasp the barbell with palms facing downwards, and maintain a straight back with engaged core muscles.
-
Lifting Action: Keep the back straight as you lift the barbell using the power of your legs and glutes, sliding it up along the inside of your thighs until reaching a standing position.
-
Peak Position: Maintain an upright posture with retracted shoulder blades and slightly bent knees.
-
Lowering Action: Lower the barbell slowly and with control, maintaining a straight back throughout the movement.
Muscles Targeted by Deadlifts
Deadlifts primarily target the following muscle groups:
- Posterior Leg Muscles: Hamstrings and Gluteus Maximus
- Core Muscles: Rectus Abdominis and External Obliques
- Back Muscles: Latissimus Dorsi and Rhomboids
- Shoulder and Arm Muscles: Deltoids and Biceps Brachii
Key Considerations During Deadlifts
To ensure safe and effective deadlifts, pay attention to the following details:
- Back Posture: Maintain an erect back with tightness throughout the movement.
- Knee Position: Keep knees slightly bent to distribute force and alleviate pressure on the knee joints.
- Arm Alignment: Depress shoulders and keep arms extended to engage back muscles.
- Center of Gravity Balance: Maintain stable heel placement for enhanced stability.
- Breathing Technique: Inhale deeply during the lifting phase and exhale slowly during the lowering phase.
- Proximity of Barbell to Body: Keep the barbell close to thighs to control the movement.
- Gradual Weight Increment: Progressively increase weight to maintain proper form.
- Focused Gaze: Maintain a forward stare to promote natural alignment of the neck and spine.
Conclusion
In essence, deadlifts offer a myriad of benefits for both physical health and athletic performance. However, mastering proper form and technique is essential for reaping these rewards safely and effectively. Whether you're a novice or seasoned lifter, incorporating deadlifts into your workout routine can lead to significant improvements in strength, stability, and overall fitness. So, embrace the challenge, focus on technique, and unlock the full potential of deadlifts in your fitness journey.